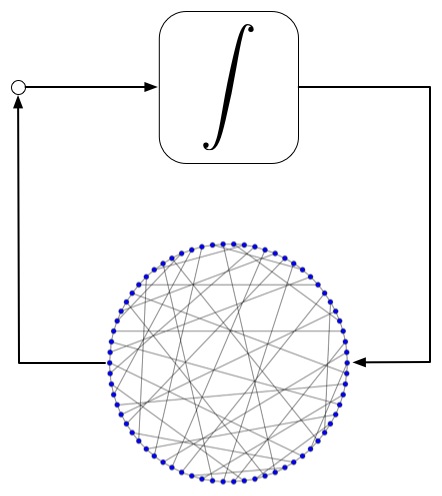
Multi-agent systems are large-scale systems comprised of a group of coupled dynamic units, such as power generation sources in a power distribution network or a team of autonomous and unmanned vehicles. These systems interact via an exchange of information over a communication and sensing network. The complexity of this general class of problems arises from the heterogeneous dynamics of the systems comprising it, the diversity of interaction and communication mediums, and their scale in terms of the number of interacting systems and system interconnections. While research in this area is very active within the controls community, there remain many challenging and open problems that must be addressed before considering this a complete theory. The fundamental research questions we are looking at are:
- How does the underlying connection topology of networked dynamic systems affect its systems-theoretic properties?
- Can the connection topology be designed in conjunction with other synthesis techniques and tools used for dynamic systems?
We explore many different research questions in this area. Below is a sample of some of our contributions.
Consensus Algorithms
A fundamental task in many multi-agent coordination problems is the ability of the agents to distributedly agree on some quantity of interest. This may include agreeing on a common heading and speed for autonomous vehicles, opinions in social networks, or estimates of measured quantities. Our works have explored how the information exchange structure between agents influences the performance of these consensus algorithms.
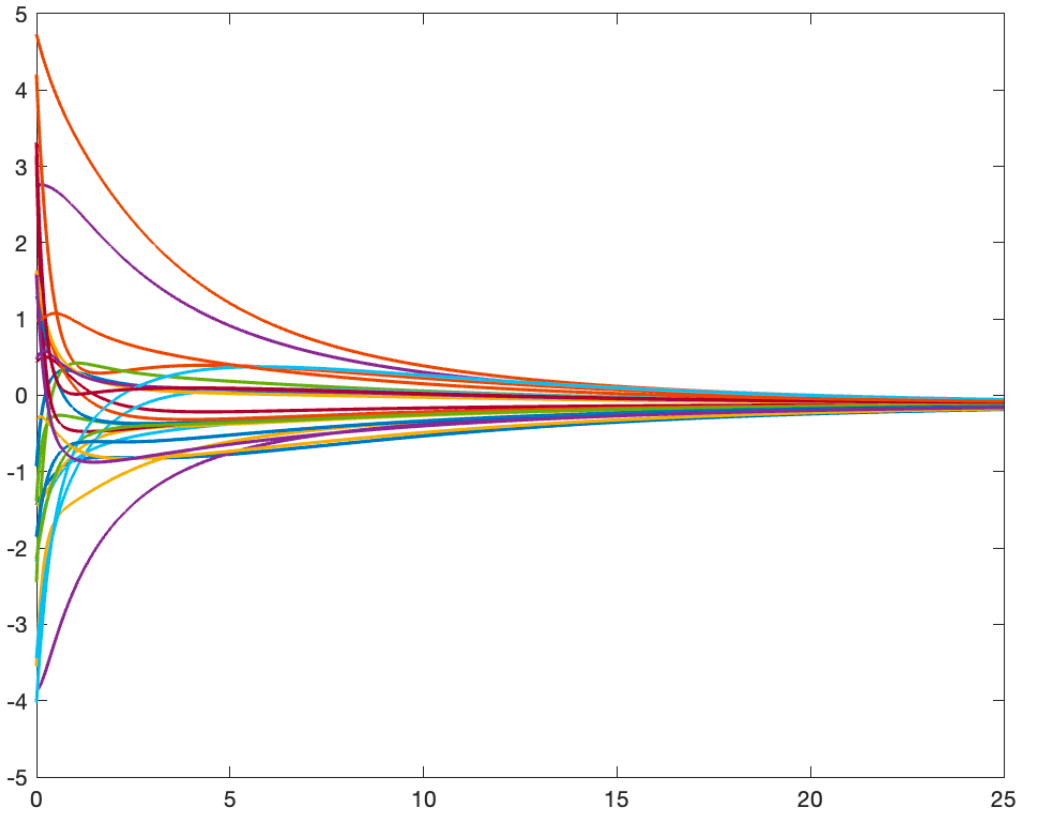
Trajectories of a consensus protocol.
Selected Publications:
- F. Yue and D. Zelazo, “A Passivity Analysis for Nonlinear Consensus on Digraphs,” in 64th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Rio de Janerio, Brazil, Dec. 2025.



@inproceedings{Yue2025_CDC,
address = {Rio de Janerio, Brazil},
author = {Yue, Fengyu and Zelazo, Daniel},
booktitle = {64th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control},
researchtopic = {passivity, nonlinearcontrol, nds, consensus},
title = {A Passivity Analysis for Nonlinear Consensus on Digraphs},
year = {2025},
pages = {6216--6221},
month = dec,
pdf = {/Publications/YUE_CDC25.pdf},
slides = {/Talks/CDC2025_Yue.pdf}
}
- G. Barkai, L. Mirkin, and D. Zelazo, “On two-degrees-of-freedom agreement protocols,” Nov. 2025.



@techreport{Barkai2026_ECC,
archiveprefix = {arXiv},
author = {Barkai, Gal and Mirkin, Leonid and Zelazo, Daniel},
eprint = {2511.12632},
journal = {arXiv},
researchtopic = {nds, consensus},
title = {On two-degrees-of-freedom agreement protocols},
arxiv = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.12632},
year = {2025},
month = nov,
pdf = {/Publications/Barkai_ECC26.pdf}
}
- G. Barkai, “Exploiting the iInterplay Between Spatial and Temporal Constraints in the Control of Multi-Agent Systems,” phdthesis, Technion - Israel Institute of Technology, Mechanical Engineering Department, 2025.


@thesis{Barkai2025,
author = {Barkai, Gal},
title = {Exploiting the iInterplay Between Spatial and Temporal Constraints in the Control of Multi-Agent Systems},
school = {Technion - Israel Institute of Technology, Mechanical Engineering Department},
year = {2025},
type = {phdthesis},
researchtopic = {thesis, nds, consensus},
pdf = {/Theses/Thesis_Barkai.pdf}
}
- G. Barkai, L. Mirkin, and D. Zelazo, “On Sampled-Data Consensus: Divide and Concur,” IEEE Control Systems Letters, 6:343–348, 2022.



@article{Barkai2022a_J,
author = {Barkai, Gal and Mirkin, Leonid and Zelazo, Daniel},
doi = {10.1109/lcsys.2021.3074589},
journal = {IEEE Control Systems Letters},
keyword = {journal},
number = {},
pages = {343--348},
researchtopic = {nds, consensus},
title = {On Sampled-Data Consensus: Divide and Concur},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/lcsys.2021.3074589},
volume = {6},
year = {2022},
pdf = {/Publications/Barkai_LCSS2022.pdf}
}
- D. Zelazo, M. Mesbahi, and M.-A. Belabbas, “Graph Theory in Systems and Controls,” in IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Miami, Florida, Dec. 2018.




@inproceedings{Zelazo2018a,
address = {Miami, Florida},
author = {Zelazo, Daniel and Mesbahi, Mehran and Belabbas, M.-A.},
booktitle = {IEEE Conference on Decision and Control},
doi = {10.1109/cdc.2018.8619841},
keywords = {conference, consensus},
month = dec,
pages = {6168--6179},
researchtopic = {nds, consensus},
title = {{Graph Theory in Systems and Controls}},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/cdc.2018.8619841},
year = {2018},
pdf = {/Publications/Zelazo_CDC2018.pdf},
slides = {/Talks/CDC2018_tutorial_slides.pdf}
}
- M. H. Trinh, D. Zelazo, Q. V. Tran, and H.-S. Ahn, “Pointing Consensus for Rooted Out-Branching Graphs,” in American Control Conference, Milwaukee, WI, Jun. 2018.



@inproceedings{Trinh2018a,
address = {Milwaukee, WI},
author = {Trinh, M. H. and Zelazo, D and Tran, Q. V. and Ahn, H-S},
booktitle = {American Control Conference},
doi = {10.23919/acc.2018.8430992},
keywords = {conference},
month = jun,
pages = {3648--3653},
researchtopic = {nds, consensus},
title = {Pointing Consensus for Rooted Out-Branching Graphs},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.23919/acc.2018.8430992},
year = {2018},
pdf = {/Publications/Trinh_ACC18.pdf}
}
- N. Leiter and D. Zelazo, “Graph-Based Model Reduction of the Controlled Consensus Protocol,” in IFAC World Congress, Toulouse, France, Jul. 2017.



@inproceedings{Leiter2017a,
address = {Toulouse, France},
author = {Leiter, Noam and Zelazo, D},
booktitle = {IFAC World Congress},
doi = {10.1016/j.ifacol.2017.08.1467},
keywords = {conference},
month = jul,
pages = {9866--9871},
researchtopic = {nds, consensus},
title = {Graph-Based Model Reduction of the Controlled Consensus Protocol},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2405896317320438},
year = {2017},
pdf = {/Publications/Leiter_IFAC17.pdf}
}
- D. Zelazo, S. Schuler, and F. Allgöwer, “Performance and Design of Cycles in Consensus Networks,” Systems & Control Letters, 62(1):85–96, 2013.



@article{Zelazo2011_J,
author = {Zelazo, Daniel and Schuler, Simone and Allg\"{o}wer, Frank},
doi = {10.1016/j.sysconle.2012.10.014},
journal = {Systems \& Control Letters},
month = jan,
number = {1},
pages = {85--96},
researchtopic = {nds, consensus},
title = {{Performance and Design of Cycles in Consensus Networks}},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.sysconle.2012.10.014},
volume = {62},
year = {2013},
pdf = {/Publications/Zelazo_SCL2013.pdf}
}
- D. Zelazo and F. Allgöwer, “Eulerian Consensus Networks,” in 51st IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Maui, HI, Dec. 2012.




@inproceedings{Zelazo2012a,
address = {Maui, HI},
author = {Zelazo, Daniel and Allg\"{o}wer, Frank},
booktitle = {51st IEEE Conference on Decision and Control},
doi = {10.1109/CDC.2012.6425921},
isbn = {978-1-4673-2066-5},
keywords = {conference},
month = dec,
pages = {4715--4720},
researchtopic = {nds, consensus},
title = {{Eulerian Consensus Networks}},
url = {http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/lpdocs/epic03/wrapper.htm?arnumber=6425921},
year = {2012},
pdf = {/Publications/Zelazo_CDC12_a.pdf},
slides = {/Talks/CDC2012_Zelazo_a}
}
- D. Zelazo and M. Mesbahi, “Edge Agreement: Graph-Theoretic Performance Bounds and Passivity Analysis,” IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 56(3):544–555, 2011.



@article{Zelazo2009b_J,
author = {Zelazo, Daniel and Mesbahi, Mehran},
doi = {10.1109/TAC.2010.2056730},
issn = {0018-9286},
journal = {IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control},
month = mar,
number = {3},
pages = {544--555},
researchtopic = {nds, graphs, consensus, passivity},
title = {{Edge Agreement: Graph-Theoretic Performance Bounds and Passivity Analysis}},
url = {http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/lpdocs/epic03/wrapper.htm?arnumber=5504814},
volume = {56},
year = {2011},
pdf = {/Publications/Zelazo_TAC2011.pdf}
}
- D. Zelazo, “Graph-theoretic Methods for the Analysis and Synthesis of Networked Dynamic Systems,” phdthesis, University of Washington, Department of Aeronautics & Astronautics, 2009.


@thesis{Zelazo2010,
author = {Zelazo, Daniel},
title = {Graph-theoretic Methods for the Analysis and Synthesis of Networked Dynamic Systems},
school = {University of Washington, Department of Aeronautics \& Astronautics},
year = {2009},
type = {phdthesis},
researchtopic = {thesis, nds, consensus},
pdf = {/Theses/Thesis_ZelazoPhD.pdf}
}
Network Identification
Many large scale networks are often designed with hopes of plug-and-play behavior. In other applications, agents in a network may be vulnerable to attack or failure resulting in changes to the network structure and behavior. As a result, the network structure may not be known. It is of interest, therefore, to try to estimate or recover the network structure using only limited measurements from the network itself. This is known as the network identification problem.
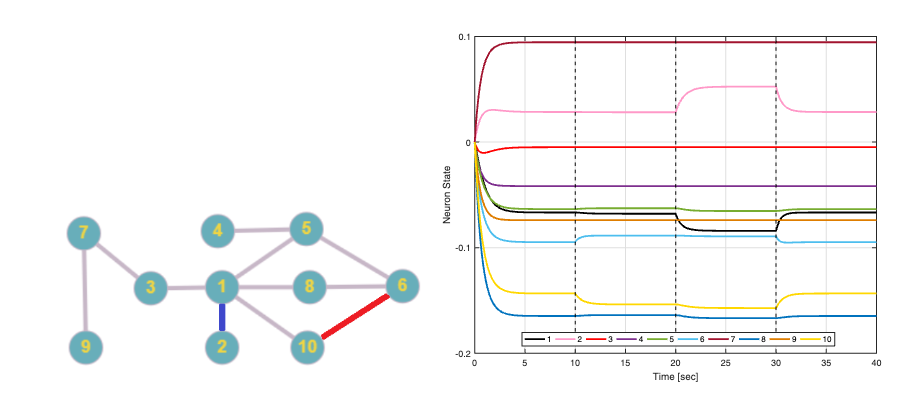
Fault identification in networks.
Selected Publications:
- M. Sharf and D. Zelazo, “Network Identification for Diffusively-Coupled Networks with Minimal Time Complexity,” IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 10(3):1616–1628, 2023.



@article{Sharf2023a_J,
author = {Sharf, Miel and Zelazo, Daniel},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1109/TCNS.2023.3237368},
journal = {IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems},
keyword = {journal},
month = sep,
number = {3},
pages = {1616--1628},
researchtopic = {nds, netID},
title = {Network Identification for Diffusively-Coupled Networks with Minimal Time Complexity},
url = {https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10018282},
volume = {10},
year = {2023},
pdf = {/Publications/Sharf_TCNS2023.pdf}
}
- D. Zelazo, M. Fabris, and L. Peled-Eitan, “Distributed Identification of Leader Agents in Semi-Autonomous Networks,” in 62nd Israel Annual Conference on Aerospace Sciences, Haifa, Israel, Mar. 2023.



@inproceedings{Zelazo2023b_C,
address = {Haifa, Israel},
author = {Zelazo, Daniel and Fabris, Marco and Peled-{Eitan}, Liat},
booktitle = {62nd Israel Annual Conference on Aerospace Sciences},
keywords = {conference},
month = mar,
pages = {},
researchtopic = {netID, nds},
title = {{Distributed Identification of Leader Agents in Semi-Autonomous Networks}},
year = {2023},
pdf = {/Publications/IACAS2023_zelazo.pdf},
slides = {/Talks/IACAS2023_zelazo_slides.pdf}
}
- M. Sharf and D. Zelazo, “Monitoring Link Faults in Nonlinear Diffusively-coupled Networks,” IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 67(6):2857–2872, 2022.



@article{Sharf2019d_J,
author = {Sharf, Miel and Zelazo, Daniel},
doi = {10.1109/tac.2021.3095258},
journal = {IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control},
keyword = {journal},
month = jun,
number = {6},
pages = {2857--2872},
researchtopic = {nds, netID},
title = {Monitoring Link Faults in Nonlinear Diffusively-coupled Networks},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/tac.2021.3095258},
volume = {67},
year = {2022},
pdf = {/Publications/Sharf_TAC2022.pdf}
}
- M. Sharf and D. Zelazo, “Network Identification: A Passivity and Network Optimization Approach,” in IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Miami, Florida, Dec. 2018.



@inproceedings{Sharf2018a,
address = {Miami, Florida},
author = {Sharf, Miel and Zelazo, Daniel},
booktitle = {IEEE Conference on Decision and Control},
doi = {10.1109/cdc.2018.8619059},
keywords = {conference},
month = dec,
pages = {2107--2113},
researchtopic = {netID, passivity},
title = {{Network Identification: A Passivity and Network Optimization Approach}},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/cdc.2018.8619059},
year = {2018},
pdf = {/Publications/Sharf_CDC18.pdf}
}
All our publications in this area can be found below:
Related Publications:
- F. Yue and D. Zelazo, “A Passivity Analysis for Nonlinear Consensus on Digraphs,” in 64th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Rio de Janerio, Brazil, Dec. 2025.



@inproceedings{Yue2025_CDC,
address = {Rio de Janerio, Brazil},
author = {Yue, Fengyu and Zelazo, Daniel},
booktitle = {64th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control},
researchtopic = {passivity, nonlinearcontrol, nds, consensus},
title = {A Passivity Analysis for Nonlinear Consensus on Digraphs},
year = {2025},
pages = {6216--6221},
month = dec,
pdf = {/Publications/YUE_CDC25.pdf},
slides = {/Talks/CDC2025_Yue.pdf}
}
- G. Barkai, L. Mirkin, and D. Zelazo, “On two-degrees-of-freedom agreement protocols,” Nov. 2025.



@techreport{Barkai2026_ECC,
archiveprefix = {arXiv},
author = {Barkai, Gal and Mirkin, Leonid and Zelazo, Daniel},
eprint = {2511.12632},
journal = {arXiv},
researchtopic = {nds, consensus},
title = {On two-degrees-of-freedom agreement protocols},
arxiv = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.12632},
year = {2025},
month = nov,
pdf = {/Publications/Barkai_ECC26.pdf}
}
- E. Matmon and D. Zelazo, “Fiedler-Based Characterization and Identification of Leaders in Semi-Autonomous Networks,” Nov. 2025.



@techreport{Matmon2026_ECC,
archiveprefix = {arXiv},
author = {Matmon, Evyatar and Zelazo, Daniel},
eprint = {2511.02317},
journal = {arXiv},
researchtopic = {nds},
title = {Fiedler-Based Characterization and Identification of Leaders in Semi-Autonomous Networks},
arxiv = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.02317},
year = {2025},
month = nov,
pdf = {/Publications/Matmon_ECC26.pdf}
}
- F. Yue and D. Zelazo, “A Passivity Analysis for Nonlinear Consensus on Balanced Digraphs,” European Journal of Control, 86(Part A):101368, 2025.




@article{Yue2025_EJC,
author = {Yue, Fengyu and Zelazo, Daniel},
researchtopic = {nds, nonlinearcontrol},
title = {A Passivity Analysis for Nonlinear Consensus on Balanced Digraphs},
year = {2025},
journal = {European Journal of Control},
number = {Part A},
month = sep,
volume = {86},
pages = {101368},
doi = {10.1016/j.ejcon.2025.101368},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0947358025001979},
pdf = {/Publications/YUE_EJC25.pdf},
slides = {/Talks/ECC25_Yue.pdf}
}
- F. Yue and D. Zelazo, “A Passivity Analysis for Nonlinear Consensus
on Digraphs,” in IAAC3 Control Conference, Herzliya, Israel, Apr. 2025.


@inproceedings{Yue_IAAC2025,
address = {Herzliya, Israel},
author = {Yue, Fengyu and Zelazo, Daniel},
booktitle = {IAAC\textsuperscript{3} Control Conference},
keywords = {conference, consensus},
month = apr,
year = {2025},
pages = {},
researchtopic = {nds},
title = {{A Passivity Analysis for Nonlinear Consensus
on Digraphs}},
slides = {/Talks/IAAC25_Yue.pdf}
}
- E. Matmon and D. Zelazo, “Leader Identification in Semi-Autonomous Consensus Protocols,” in IAAC3 Control Conference, Herzliya, Israel, Apr. 2025.


@inproceedings{Matmon_IAAC2025,
address = {Herzliya, Israel},
author = {Matmon, Evyatar and Zelazo, Daniel},
booktitle = {IAAC\textsuperscript{3} Control Conference},
keywords = {conference, consensus},
month = apr,
year = {2025},
pages = {},
researchtopic = {nds},
title = {{Leader Identification in Semi-Autonomous Consensus Protocols}},
slides = {/Talks/IAAC25_Matmon.pdf}
}
- G. Barkai, L. Mirkin, and D. Zelazo, “On Filtered Consensus Protocols,” in IAAC3 Control Conference, Herzliya, Israel, Apr. 2025.

@inproceedings{Barkai_IAAC2025,
address = {Herzliya, Israel},
author = {Barkai, Gal and Mirkin, Leonid and Zelazo, Daniel},
booktitle = {IAAC\textsuperscript{3} Control Conference},
keywords = {conference, consensus},
month = apr,
year = {2025},
pages = {},
researchtopic = {nds},
title = {{On Filtered Consensus Protocols}}
}
- M. Sharf and D. Zelazo, “Cluster assignment in multi-agent systems: Sparsity bounds and fault tolerance,” Asian Journal of Control, 27(1):63–75, 2025.



@article{Sharf2025a_J,
author = {Sharf, Miel and Zelazo, Daniel},
doi = {10.1002/asjc.3149},
journal = {Asian Journal of Control},
keywords = {clustering, diffusive coupling, fault tolerance, graph theory, multi-agent networks, sparsity},
researchtopic = {nds, robust},
title = {Cluster assignment in multi-agent systems: Sparsity bounds and fault tolerance},
url = {https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/asjc.3149},
year = {2025},
volume = {27},
number = {1},
pages = {63--75},
pdf = {/Publications/Sharf_AJC2025.pdf}
}
- G. Barkai, “Exploiting the iInterplay Between Spatial and Temporal Constraints in the Control of Multi-Agent Systems,” phdthesis, Technion - Israel Institute of Technology, Mechanical Engineering Department, 2025.


@thesis{Barkai2025,
author = {Barkai, Gal},
title = {Exploiting the iInterplay Between Spatial and Temporal Constraints in the Control of Multi-Agent Systems},
school = {Technion - Israel Institute of Technology, Mechanical Engineering Department},
year = {2025},
type = {phdthesis},
researchtopic = {thesis, nds, consensus},
pdf = {/Theses/Thesis_Barkai.pdf}
}
- E. Matmon, “Leader Identification of Multi-Agents Systems Under Semi-Autonomous Consensus Protocol,” mastersthesis, Technion - Israel Institute of Technology, Autonomous Systems and Robotics, 2025.

@thesis{Matmon2025,
author = {Matmon, Evyatar},
title = {Leader Identification of Multi-Agents Systems Under Semi-Autonomous Consensus Protocol},
school = {Technion - Israel Institute of Technology, Autonomous Systems and Robotics},
year = {2025},
type = {mastersthesis},
researchtopic = {thesis, nds}
}
- G. Barkai, L. Mirkin, and D. Zelazo, “Asynchronous Sampled-Data Synchronization with Small Communications Delays,” in IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Milan, Italy, Dec. 2024.




@inproceedings{Barkai2024_CDC,
address = {Milan, Italy},
author = {Barkai, Gal and Mirkin, Leonid and Zelazo, Daniel},
booktitle = {IEEE Conference on Decision and Control},
keywords = {conference},
month = dec,
pages = {1619--1624},
researchtopic = {nds, eventtrigger},
title = {{Asynchronous Sampled-Data Synchronization with Small Communications Delays}},
slides = {/Talks/CDC2024_Barkai.pdf},
year = {2024},
doi = {10.1109/CDC56724.2024.10886376},
pdf = {/Publications/Barkai_CDC24.pdf}
}
- G. Barkai, L. Mirkin, and D. Zelazo, “An Emulation Approach to Output-Feedback Sampled-Data Synchronization,” in European Control Conference, Stockholm, Sweden, Jun. 2024.



@inproceedings{Barkai2024_ECC,
address = {Stockholm, Sweden},
author = {Barkai, Gal and Mirkin, Leonid and Zelazo, Daniel},
booktitle = {European Control Conference},
keywords = {conference},
month = jun,
pages = {2610--2615},
researchtopic = {nds,eventtrigger},
title = {{An Emulation Approach to Output-Feedback Sampled-Data Synchronization}},
year = {2024},
slides = {/Talks/ECC2024_Barkai.pdf},
pdf = {/Publications/Barkai_ECC24.pdf}
}
- J. Shi and D. Zelazo, “Bearing-only Formation Control with Directed Sensing,” in 63rd Israel Annual Conference on Aerospace Sciences, Haifa, Israel, May 2024.



@inproceedings{Shi_IACAS2024,
address = {Haifa, Israel},
author = {Shi, Jiacheng and Zelazo, Daniel},
booktitle = {63rd Israel Annual Conference on Aerospace Sciences},
keywords = {conference, consensus},
month = may,
year = {2024},
pages = {},
researchtopic = {nds, formationcontrol},
title = {{Bearing-only Formation Control with Directed Sensing}},
slides = {/Talks/Shi_IACAS2024.pdf},
pdf = {/Publications/Shi_IACAS2024.pdf}
}
- J. Attias, Y. Marciano, R. Arhipov, and D. Zelazo, “An Open Source Quadcopter Platform for Simulink,” in 63rd Israel Annual Conference on Aerospace Sciences, Haifa, Israel, May 2024.



@inproceedings{Attias_IACAS2024,
address = {Haifa, Israel},
author = {Attias, Joseph and Marciano, Yael and Arhipov, Ruslan and Zelazo, Daniel},
booktitle = {63rd Israel Annual Conference on Aerospace Sciences},
keywords = {conference, consensus},
month = may,
year = {2024},
pages = {},
researchtopic = {nds, robotics},
title = {{An Open Source Quadcopter Platform for Simulink}},
slides = {/Talks/DroneLab_IACAS_2024.pdf},
pdf = {/Publications/Attias_IACAS2024.pdf}
}
- F. Yue and D. Zelazo, “Diodes and the Importance of Network Orientations in Diffusively-Coupled Networks,” in 63rd Israel Annual Conference on Aerospace Sciences, Haifa, Israel, May 2024.



@inproceedings{Yue_IACAS2024,
address = {Haifa, Israel},
author = {Yue, Fengyu and Zelazo, Daniel},
booktitle = {63rd Israel Annual Conference on Aerospace Sciences},
keywords = {conference, consensus},
month = may,
year = {2024},
pages = {},
researchtopic = {nds},
title = {{Diodes and the Importance of Network Orientations in Diffusively-Coupled Networks}},
slides = {/Talks/Yue_IACAS2024.pdf},
pdf = {/Publications/Yue_IACAS2024.pdf}
}
- G. Barkai, L. Mirkin, and D. Zelazo, “Asynchronous Sampled-Data Synchronization with Small communication Delays,” in 63rd Israel Annual Conference on Aerospace Sciences, Haifa, Israel, May 2024.


@inproceedings{Barkai_IACAS2024,
address = {Haifa, Israel},
author = {Barkai, Gal and Mirkin, Leonid and Zelazo, Daniel},
booktitle = {63rd Israel Annual Conference on Aerospace Sciences},
keywords = {conference, consensus},
month = may,
year = {2024},
pages = {},
researchtopic = {nds, eventtrigger},
title = {{Asynchronous Sampled-Data Synchronization with Small communication Delays}},
pdf = {/Publications/Barkai_IACAS2024.pdf}
}
- G. Barkai, L. Mirkin, and D. Zelazo, “An emulation approach to sampled-data synchronization,” in IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Singapore, Dec. 2023.



@inproceedings{Barkai2023a,
address = {Singapore},
author = {Barkai, Gal and Mirkin, Leonid and Zelazo, Daniel},
booktitle = {IEEE Conference on Decision and Control},
doi = {10.1109/cdc49753.2023.10384079},
keywords = {conference},
month = dec,
pages = {6449--6454},
researchtopic = {nds, eventtrigger},
title = {{An emulation approach to sampled-data synchronization}},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/cdc49753.2023.10384079},
year = {2023},
pdf = {/Publications/Barkai_CDC2023.pdf}
}
- G. Barkai, L. Mirkin, and D. Zelazo, “On the internal stability of diffusively coupled multi-agent systems and the dangers of cancel culture,” Automatica, 155:111158, 2023.



@article{Barkai2023a_J,
author = {Barkai, Gal and Mirkin, Leonid and Zelazo, Daniel},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.automatica.2023.111158},
issn = {0005-1098},
journal = {Automatica},
keyword = {journal},
keywords = {Multi-agent systems, Controller constraints and structure, Stability},
month = sep,
pages = {111158},
researchtopic = {nds},
title = {On the internal stability of diffusively coupled multi-agent systems and the dangers of cancel culture},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0005109823003199},
volume = {155},
year = {2023},
pdf = {/Publications/Barkai_AUT2023.pdf}
}
- M. Sharf and D. Zelazo, “Network Identification for Diffusively-Coupled Networks with Minimal Time Complexity,” IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 10(3):1616–1628, 2023.



@article{Sharf2023a_J,
author = {Sharf, Miel and Zelazo, Daniel},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1109/TCNS.2023.3237368},
journal = {IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems},
keyword = {journal},
month = sep,
number = {3},
pages = {1616--1628},
researchtopic = {nds, netID},
title = {Network Identification for Diffusively-Coupled Networks with Minimal Time Complexity},
url = {https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10018282},
volume = {10},
year = {2023},
pdf = {/Publications/Sharf_TCNS2023.pdf}
}
- M.-A. Belabbas, X. Chen, and D. Zelazo, “On Structural Rank and Resilience of Sparsity Patterns,” IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 68(8):4783–4795, 2023.



@article{Belabbas2021a_J,
author = {Belabbas, M-A and Chen, Xudong and Zelazo, Daniel},
doi = {10.1109/tac.2022.3212013},
journal = {IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control},
keyword = {journal},
month = aug,
number = {8},
pages = {4783 - 4795},
researchtopic = {graphs, nds, robust},
title = {On Structural Rank and Resilience of Sparsity Patterns},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/tac.2022.3212013},
volume = {68},
year = {2023},
pdf = {/Publications/Belabbas_TAC2023.pdf}
}
- A. Priel and D. Zelazo, “Event-triggered consensus Kalman filtering for time-varying networks and intermittent observations,” International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 33(13):7430–7451, 2023.



@article{Priel2023_J,
author = {Priel, Aviv and Zelazo, Daniel},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1002/rnc.6762},
eprint = {https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/rnc.6762},
journal = {International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control},
keyword = {journal},
keywords = {distributed estimation, event-triggered estimation, multi-agent systems, sensor networks},
month = may,
number = {13},
pages = {7430-7451},
researchtopic = {nds, eventtrigger},
title = {Event-triggered consensus Kalman filtering for time-varying networks and intermittent observations},
url = {https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/rnc.6762},
volume = {33},
year = {2023},
pdf = {/Publications/Priel_IJRNC2023.pdf}
}
- D. Zelazo, M. Fabris, and L. Peled-Eitan, “Distributed Identification of Leader Agents in Semi-Autonomous Networks,” in 62nd Israel Annual Conference on Aerospace Sciences, Haifa, Israel, Mar. 2023.



@inproceedings{Zelazo2023b_C,
address = {Haifa, Israel},
author = {Zelazo, Daniel and Fabris, Marco and Peled-{Eitan}, Liat},
booktitle = {62nd Israel Annual Conference on Aerospace Sciences},
keywords = {conference},
month = mar,
pages = {},
researchtopic = {netID, nds},
title = {{Distributed Identification of Leader Agents in Semi-Autonomous Networks}},
year = {2023},
pdf = {/Publications/IACAS2023_zelazo.pdf},
slides = {/Talks/IACAS2023_zelazo_slides.pdf}
}
- M. Fabris and D. Zelazo, “A Robustness Analysis to Structured Channel Tampering Over Secure-by-Design Consensus Networks,” IEEE Control Systems Letters, 7:2011–2016, 2023.




@article{Fabris2023_J,
author = {Fabris, Marco and Zelazo, Daniel},
doi = {10.1109/LCSYS.2023.3284482},
journal = {IEEE Control Systems Letters},
keyword = {journal},
number = {},
pages = {2011-2016},
researchtopic = {nds, robust},
title = {A Robustness Analysis to Structured Channel Tampering Over Secure-by-Design Consensus Networks},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/lcsys.2023.3284482},
volume = {7},
year = {2023},
pdf = {/Publications/Fabris_LCSS2023.pdf},
slides = {/Talks/CDC2023_Fabris.pdf}
}
- G. Barkai, L. Mirkin, and D. Zelazo, “On Internal Stability of Diffusive-Coupling and the Dangers of Cancel Culture,” in 25th International Symposium on Mathematical Theory of Networks and Systems, Germany, Sep. 2022.



@inproceedings{Barkai2022a,
address = {Germany},
author = {Barkai, Gal and Mirkin, Leonid and Zelazo, Daniel},
booktitle = {25th International Symposium on Mathematical Theory of Networks and Systems},
keywords = {conference},
month = sep,
pages = {},
researchtopic = {nds},
title = {{On Internal Stability of Diffusive-Coupling and the Dangers of Cancel Culture}},
year = {2022},
slides = {/Talks/MTNS2022_Barkai.pdf},
pdf = {/Publications/Barkai_MTNS2022.pdf}
}
- M. Fabris and D. Zelazo, “Secure Consensus via Objective Coding: Robustness Analysis to Channel Tampering,” IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man and Cybernetics: Systems, 52(12):7885–7897, 2022.



@article{Fabris2022a_J,
author = {Fabris, Marco and Zelazo, Daniel},
doi = {10.1109/tsmc.2022.3177756},
journal = {IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man and Cybernetics: Systems},
keyword = {journal},
month = jun,
number = {12},
pages = {7885--7897},
researchtopic = {nds, robust},
title = {Secure Consensus via Objective Coding: Robustness Analysis to Channel Tampering},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/tsmc.2022.3177756},
volume = {52},
year = {2022},
pdf = {/Publications/Fabris_SMCS2022.pdf}
}
- M. Sharf and D. Zelazo, “Monitoring Link Faults in Nonlinear Diffusively-coupled Networks,” IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 67(6):2857–2872, 2022.



@article{Sharf2019d_J,
author = {Sharf, Miel and Zelazo, Daniel},
doi = {10.1109/tac.2021.3095258},
journal = {IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control},
keyword = {journal},
month = jun,
number = {6},
pages = {2857--2872},
researchtopic = {nds, netID},
title = {Monitoring Link Faults in Nonlinear Diffusively-coupled Networks},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/tac.2021.3095258},
volume = {67},
year = {2022},
pdf = {/Publications/Sharf_TAC2022.pdf}
}
- M. Sharf and D. Zelazo, “Cluster Assignment in Multi-Agent Systems,” in The 13th Asian Control Conference, Jeju Island, South Korea, May 2022.




@inproceedings{Sharf2022a,
address = {Jeju Island, South Korea},
author = {Sharf, Miel and Zelazo, Daniel},
booktitle = {The 13th Asian Control Conference},
doi = {10.23919/ascc56756.2022.9828091},
keywords = {conference},
month = may,
pages = {947--952},
researchtopic = {nds},
title = {{Cluster Assignment in Multi-Agent Systems}},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.23919/ascc56756.2022.9828091},
year = {2022},
slides = {/Talks/ASCC2022.pdf},
pdf = {/Publications/Sharf_ASCC2022.pdf}
}
- M. Sharf, A. Romer, D. Zelazo, and F. Allgower, “Model-Free Practical Cooperative Control for Diffusively Coupled Systems,” IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 67(2):754–766, 2022.



@article{Sharf2019e_J,
author = {Sharf, Miel and Romer, Anne and Zelazo, Daniel and Allgower, Frank},
doi = {10.1109/tac.2021.3056582},
journal = {IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control},
keyword = {journal},
month = feb,
number = {2},
pages = {754--766},
researchtopic = {nds, datadriven},
title = {Model-Free Practical Cooperative Control for Diffusively Coupled Systems},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/tac.2021.3056582},
volume = {67},
year = {2022},
pdf = {/Publications/Sharf_TAC2022b.pdf}
}
- G. Barkai, L. Mirkin, and D. Zelazo, “On Sampled-Data Consensus: Divide and Concur,” IEEE Control Systems Letters, 6:343–348, 2022.



@article{Barkai2022a_J,
author = {Barkai, Gal and Mirkin, Leonid and Zelazo, Daniel},
doi = {10.1109/lcsys.2021.3074589},
journal = {IEEE Control Systems Letters},
keyword = {journal},
number = {},
pages = {343--348},
researchtopic = {nds, consensus},
title = {On Sampled-Data Consensus: Divide and Concur},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/lcsys.2021.3074589},
volume = {6},
year = {2022},
pdf = {/Publications/Barkai_LCSS2022.pdf}
}
- N. Leiter, “Graph-based Model Reduction Methods for Multi-Agent Systems,” phdthesis, Technion - Israel Institute of Technology, Aerospace Engineering Department, 2022.


@thesis{Leiter2022,
author = {Leiter, Noam},
title = {Graph-based Model Reduction Methods for Multi-Agent Systems},
school = {Technion - Israel Institute of Technology, Aerospace Engineering Department},
year = {2022},
type = {phdthesis},
researchtopic = {thesis, nds, graph},
pdf = {/Theses/Thesis_Leiter.pdf}
}
- A. Priel, “Consensus Kalman Filtering: Filter Design and Event-Triggering,” mastersthesis, Technion - Israel Institute of Technology, Aerospace Engineering Department, 2022.


@thesis{Priel2022,
author = {Priel, Aviv},
title = {Consensus Kalman Filtering: Filter Design and Event-Triggering},
school = {Technion - Israel Institute of Technology, Aerospace Engineering Department},
year = {2022},
type = {mastersthesis},
researchtopic = {thesis, nds, eventtrigger},
pdf = {/Theses/Thesis_Priel.pdf}
}
- A. Priel and D. Zelazo, “An Improved Distributed Consensus Kalman Filter Design Approach,” in IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Austin, Texas, Dec. 2021.




@inproceedings{Priel2021a,
address = {Austin, Texas},
author = {Priel, Aviv and Zelazo, Daniel},
booktitle = {IEEE Conference on Decision and Control},
doi = {10.1109/cdc45484.2021.9683438},
keywords = {conference},
month = dec,
pages = {502--507},
researchtopic = {eventtrigger, nds},
title = {{An Improved Distributed Consensus Kalman Filter Design Approach}},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/cdc45484.2021.9683438},
year = {2021},
slides = {/Talks/CD2021_Priel.pdf},
pdf = {/Publications/Priel_CDC21.pdf}
}
- M. Sharf, A. Jain, and D. Zelazo, “Geometric Method for Passivation and Cooperative Control of Equilibrium-Independent Passive-Short Systems,” IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 66(12):5877–5892, 2021.



@article{Sharf2019c_J,
author = {Sharf, Miel and Jain, Anoop and Zelazo, Daniel},
doi = {10.1109/tac.2020.3043390},
journal = {IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control},
keyword = {journal},
month = dec,
number = {12},
pages = {5877--5892},
researchtopic = {passivity, nonlinearcontrol, nds},
title = {Geometric Method for Passivation and Cooperative Control of Equilibrium-Independent Passive-Short Systems},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/tac.2020.3043390},
volume = {66},
year = {2021},
pdf = {/Publications/Sharf_TAC2021.pdf}
}
- N. Leiter and D. Zelazo, “Edge-matching graph contractions and their interlacing properties,” Linear Algebra and its Applications, 612:289–317, 2021.



@article{Leiter2021_J,
author = {Leiter, Noam and Zelazo, Daniel},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.laa.2020.11.003},
issn = {0024-3795},
journal = {Linear Algebra and its Applications},
keyword = {journal},
pages = {289-317},
researchtopic = {nds, graphs},
title = {Edge-matching graph contractions and their interlacing properties},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024379520305280},
volume = {612},
year = {2021},
pdf = {/Publications/Leiter_LAA2021.pdf}
}
- N. Leiter and D. Zelazo, “Product Form of Projection-Based Model Reduction and its Application to Multi-Agent Systems,” 2021.



@techreport{leiter2021product,
title = {Product Form of Projection-Based Model Reduction and its Application to Multi-Agent Systems},
author = {Leiter, Noam and Zelazo, Daniel},
year = {2021},
journal = {ArXiv e-prints},
eprint = {2112.15182},
archiveprefix = {arXiv},
arxiv = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.15182},
researchtopic = {nds, modelreduction},
pdf = {/Publications/Leiter_arxiv2021.pdf}
}
- H. Chen, D. Zelazo, X. Wang, and L. Shen, “Convergence Analysis of Signed Nonlinear Networks,” IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 7(1):189–200, 2020.



@article{Chen2018a_J,
author = {Chen, {Hao} and Zelazo, Daniel and Wang, Xiangke and Shen, {Lincheng}},
doi = {10.1109/tcns.2019.2913550},
journal = {IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems},
keyword = {journal},
month = apr,
number = {1},
pages = {189--200},
researchtopic = {nds},
title = {Convergence Analysis of Signed Nonlinear Networks},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/tcns.2019.2913550},
volume = {7},
year = {2020},
pdf = {/Publications/Chen_TCNS2020.pdf}
}
- M. Sharf, “Network Optimization Methods in Passivity-Based Cooperative Control,” phdthesis, Technion - Israel Institute of Technology, Aerospace Engineering Department, 2020.


@thesis{Sharf2020,
author = {Sharf, Miel},
title = {Network Optimization Methods in Passivity-Based Cooperative Control},
school = {Technion - Israel Institute of Technology, Aerospace Engineering Department},
year = {2020},
type = {phdthesis},
researchtopic = {thesis, nds, optimization, passivity},
pdf = {/Theses/Thesis_Sharf.pdf}
}
- Y. Palti, “Deployment Strategies for Coverage Control Problems,” mastersthesis, Technion - Israel Institute of Technology, Aerospace Engineering Department, 2020.


@thesis{Palti2020,
author = {Palti, Yoav},
title = {Deployment Strategies for Coverage Control Problems},
school = {Technion - Israel Institute of Technology, Aerospace Engineering Department},
year = {2020},
type = {mastersthesis},
researchtopic = {thesis, nds},
pdf = {/Theses/Thesis_Palti.pdf}
}
- D. Mukherjee and D. Zelazo, “Robustness of Consensus over Weighted Digraphs,” IEEE Transactions on Network Sciences and Engineering, 6(4):657–670, 2019.



@article{Muhkerjee2017a_J,
author = {Mukherjee, Dwaipayan and Zelazo, Daniel},
doi = {10.1109/tnse.2018.2866780},
journal = {IEEE Transactions on Network Sciences and Engineering},
month = dec,
number = {4},
pages = {657--670},
researchtopic = {nds, graphs, robust},
title = {Robustness of Consensus over Weighted Digraphs},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/tnse.2018.2866780},
volume = {6},
year = {2019},
pdf = {/Publications/Muhkerejee_TNSE2017.pdf}
}
- D. Mukherjee and D. Zelazo, “Consensus of Higher Order Agents: Robustness and Heterogeneity,” IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 6(4):1323–1333, 2019.



@article{Muhkerjee2017b_J,
author = {Mukherjee, Dwaipayan and Zelazo, Daniel},
doi = {10.1109/tcns.2018.2889003},
journal = {IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems},
keyword = {journal},
month = dec,
number = {4},
pages = {1323--1333},
researchtopic = {nds, robust},
title = {Consensus of Higher Order Agents: Robustness and Heterogeneity},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/tcns.2018.2889003},
volume = {6},
year = {2019},
pdf = {/Publications/Mukherjee_TCNS2019.pdf}
}
- M. Sharf and D. Zelazo, “Analysis and Synthesis of MIMO Multi-Agent Systems Using Network Optimization,” IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 64(11):1558–2523, 2019.



@article{Sharf2017b_J,
author = {Sharf, Miel and Zelazo, Daniel},
doi = {10.1109/tac.2019.2908258},
journal = {IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control},
keyword = {journal},
month = nov,
number = {11},
pages = {1558--2523},
researchtopic = {nds, passivity, optimization, nonlinearcontrol},
title = {Analysis and Synthesis of MIMO Multi-Agent Systems Using Network Optimization},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/tac.2019.2908258},
volume = {64},
year = {2019},
pdf = {/Publications/Sharf_TAC2019.pdf}
}
- M. Sharf and D. Zelazo, “Symmetry-Induced Clustering in Multi-Agent Systems using Network Optimization and Passivity,” in 27th Mediterranean Conference on Control and Automation, Akko, Israel, Jul. 2019.




@inproceedings{Sharf2019a,
address = {Akko, Israel},
author = {Sharf, Miel and Zelazo, Daniel},
booktitle = {27th Mediterranean Conference on Control and Automation},
doi = {10.1109/med.2019.8798507},
keywords = {conference},
month = jul,
pages = {13--18},
researchtopic = {nds, passivity, optimization},
title = {{Symmetry-Induced Clustering in Multi-Agent Systems using Network Optimization and Passivity}},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/med.2019.8798507},
year = {2019},
slides = {/Talks/MED2019_Sharf.pdf},
pdf = {/Publications/Sharf_MED19.pdf}
}
- M. Sharf and D. Zelazo, “Network Feedback Passivation of Passivity-Short Multi-Agent Systems,” IEEE Control Systems Letters, 3(3):607–612, 2019.




@article{Sharf2019a_J,
author = {Sharf, Miel and Zelazo, Daniel},
doi = {10.1109/lcsys.2019.2914128},
journal = {IEEE Control Systems Letters},
keyword = {journal},
month = jul,
number = {3},
pages = {607--612},
researchtopic = {passivity, nonlinearcontrol, nds},
title = {Network Feedback Passivation of Passivity-Short Multi-Agent Systems},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/lcsys.2019.2914128},
volume = {3},
year = {2019},
pdf = {/Publications/Sharf_LCSS2019.pdf},
slides = {/Talks/Sharf_CDC2019.pdf}
}
- Y. Palti and D. Zelazo, “A Projected Lloyd’s Algorithm for Coverage Control Problems,” in 59th Israel Annual Conference on Aerospace Sciences, Haifa, Israel, Mar. 2019.


@inproceedings{Palti2019a,
address = {Haifa, Israel},
author = {Palti, Yoav and Zelazo, Daniel},
booktitle = {59th Israel Annual Conference on Aerospace Sciences},
keywords = {conference},
month = mar,
pages = {1008-1022},
researchtopic = {nds},
title = {{A Projected Lloyd’s Algorithm for Coverage Control Problems}},
year = {2019},
pdf = {/Publications/Palti_IACAS2019.pdf}
}
- D. Zelazo, M. Mesbahi, and M.-A. Belabbas, “Graph Theory in Systems and Controls,” in IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Miami, Florida, Dec. 2018.




@inproceedings{Zelazo2018a,
address = {Miami, Florida},
author = {Zelazo, Daniel and Mesbahi, Mehran and Belabbas, M.-A.},
booktitle = {IEEE Conference on Decision and Control},
doi = {10.1109/cdc.2018.8619841},
keywords = {conference, consensus},
month = dec,
pages = {6168--6179},
researchtopic = {nds, consensus},
title = {{Graph Theory in Systems and Controls}},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/cdc.2018.8619841},
year = {2018},
pdf = {/Publications/Zelazo_CDC2018.pdf},
slides = {/Talks/CDC2018_tutorial_slides.pdf}
}
- A. Jain, M. Sharf, and D. Zelazo, “Regularization and Feedback Passivation in Cooperative Control of Passivity-Short Systems: A Network Optimization Perspective,” IEEE Control Systems Letters, 2(4):731–736, 2018.



@article{Jain2018a_J,
author = {Jain, Anoop and Sharf, Miel and Zelazo, Daniel},
doi = {10.1109/lcsys.2018.2847738},
journal = {IEEE Control Systems Letters},
keyword = {journal},
month = jul,
number = {4},
pages = {731--736},
researchtopic = {passivity, nonlinearcontrol, nds, optimization},
title = {Regularization and Feedback Passivation in Cooperative Control of Passivity-Short Systems: A Network Optimization Perspective},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/lcsys.2018.2847738},
volume = {2},
year = {2018},
pdf = {/Publications/Jain_LCSS2018.pdf}
}
- M. H. Trinh, D. Zelazo, Q. V. Tran, and H.-S. Ahn, “Pointing Consensus for Rooted Out-Branching Graphs,” in American Control Conference, Milwaukee, WI, Jun. 2018.



@inproceedings{Trinh2018a,
address = {Milwaukee, WI},
author = {Trinh, M. H. and Zelazo, D and Tran, Q. V. and Ahn, H-S},
booktitle = {American Control Conference},
doi = {10.23919/acc.2018.8430992},
keywords = {conference},
month = jun,
pages = {3648--3653},
researchtopic = {nds, consensus},
title = {Pointing Consensus for Rooted Out-Branching Graphs},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.23919/acc.2018.8430992},
year = {2018},
pdf = {/Publications/Trinh_ACC18.pdf}
}
- D. Mukherjee and D. Zelazo, “Robust Consensus of Higher Order Agents over Cycle Graphs,” in 58th Israel Annual Conference on Aerospace Sciences, Haifa, Israel, Mar. 2018.



@inproceedings{Mukherjee2016a,
address = {Haifa, Israel},
author = {Mukherjee, Dwaipayan and Zelazo, Daniel},
booktitle = {58th Israel Annual Conference on Aerospace Sciences},
keywords = {conference},
month = mar,
pages = {},
researchtopic = {nds, robust},
title = {{Robust Consensus of Higher Order Agents over Cycle Graphs}},
year = {2018},
slides = {/Talks/IACAS2018_Mukherjee.pdf},
pdf = {/Publications/Mukherjee_IACAS2018.pdf}
}
- N. Leiter and D. Zelazo, “The Aggregating Consensus Protocol: A Case Study of Behavioral Multi-Agent Systems,” in 58th Israel Annual Conference on Aerospace Sciences, Haifa, Israel, Feb. 2018.


@inproceedings{Leiter2018a,
address = {Haifa, Israel},
author = {Leiter, Noam and Zelazo, Daniel},
booktitle = {58th Israel Annual Conference on Aerospace Sciences},
keywords = {conference, consensus},
month = feb,
pages = {},
researchtopic = {nds},
title = {{The Aggregating Consensus Protocol: A Case Study of Behavioral Multi-Agent Systems}},
year = {2018},
pdf = {/Publications/Leiter_IACAS2018.pdf}
}
- N. Leiter and D. Zelazo, “Graph-Based Model Reduction of the Controlled Consensus Protocol,” in IFAC World Congress, Toulouse, France, Jul. 2017.



@inproceedings{Leiter2017a,
address = {Toulouse, France},
author = {Leiter, Noam and Zelazo, D},
booktitle = {IFAC World Congress},
doi = {10.1016/j.ifacol.2017.08.1467},
keywords = {conference},
month = jul,
pages = {9866--9871},
researchtopic = {nds, consensus},
title = {Graph-Based Model Reduction of the Controlled Consensus Protocol},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2405896317320438},
year = {2017},
pdf = {/Publications/Leiter_IFAC17.pdf}
}
- M. Sharf and D. Zelazo, “A Network Optimization Approach to Cooperative Control Synthesis,” IEEE Control Systems Letters, 1(1):86–91, 2017.



@article{Sharf2017a_J,
author = {Sharf, Miel and Zelazo, Daniel},
doi = {10.1109/lcsys.2017.2706948},
journal = {IEEE Control Systems Letters},
month = jul,
number = {1},
pages = {86--91},
researchtopic = {nds, optimization, nonlinearcontrol, passivity},
title = {A Network Optimization Approach to Cooperative Control Synthesis},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/lcsys.2017.2706948},
volume = {1},
year = {2017},
pdf = {/Publications/Sharf_LCSS2017.pdf}
}
- D. Zelazo and M. Bürger, “On the Robustness of Uncertain Consensus Networks,” IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 4(2):170–178, 2017.



@article{Zelazo2014a_J,
author = {{Zelazo}, D. and {B{\"u}rger}, M.},
doi = {10.1109/tcns.2015.2485458},
journal = {IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems},
keywords = {Mathematics - Optimization and Control},
month = jun,
number = {2},
pages = {170--178},
researchtopic = {nds, robust},
title = {{On the Robustness of Uncertain Consensus Networks}},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/tcns.2015.2485458},
volume = {4},
year = {2017},
pdf = {/Publications/Zelazo_TCNS2014.pdf}
}
- Y. Ben Shoushan and D. Zelazo, “Negotiation Between Dynamical Systems with Connectivity Constraints,” in 57th Israel Annual Conference on Aerospace Sciences , Tel-Aviv, Israel, Feb. 2017.


@inproceedings{Shoushan2017,
address = {Tel-Aviv, Israel},
author = {{Ben Shoushan}, Y and Zelazo, D},
booktitle = {57th Israel Annual Conference on Aerospace Sciences },
keywords = {conference},
month = feb,
pages = {},
researchtopic = {nds, optimization},
title = {Negotiation Between Dynamical Systems with Connectivity Constraints},
pdf = {/Publications/Shoushan_IACAS2017.pdf},
year = {2017}
}
- Y. Ben-Shoushan, “Negotiation between Dynamical Systems with Connectivity Constraints,” mastersthesis, Technion - Israel Institute of Technology, Aerospace Engineering Department, 2017.


@thesis{BenShoushan2017,
author = {Ben-Shoushan, Yaniv},
title = {Negotiation between Dynamical Systems with Connectivity Constraints},
school = {Technion - Israel Institute of Technology, Aerospace Engineering Department},
year = {2017},
type = {mastersthesis},
researchtopic = {thesis, nds, optimization},
pdf = {/Theses/Thesis_BenShoushan.pdf}
}
- D. Mukherjee and D. Zelazo, “Consensus Over Weighted Digraphs: A Robustness Perspective,” in 55th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Las Vegas, Nevada, Dec. 2016.



@inproceedings{Mukherjee2016b,
address = {Las Vegas, Nevada},
author = {Mukherjee, Dwaipayan and Zelazo, Daniel},
booktitle = {55th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control},
doi = {10.1109/cdc.2016.7798784},
keywords = {conference},
month = dec,
pages = {3438--3443},
researchtopic = {nds, robust},
title = {{Consensus Over Weighted Digraphs: A Robustness Perspective}},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/cdc.2016.7798784},
year = {2016},
pdf = {/Publications/Mukherjee_CDC16.pdf}
}
- D. Zelazo and M. Bürger, “On the Definiteness of the Weighted Laplacian and its Connection to Effective Resistance,” in 53rd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Los Angeles, CA, Dec. 2014.




@inproceedings{Zelazo2014f,
address = {Los Angeles, CA},
author = {Zelazo, Daniel and B\"{u}rger, Mathias},
booktitle = {53rd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control},
doi = {10.1109/cdc.2014.7039834},
keywords = {conference},
month = dec,
pages = {2895--2900},
researchtopic = {nds, graphs},
title = {{On the Definiteness of the Weighted Laplacian and its Connection to Effective Resistance}},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/cdc.2014.7039834},
year = {2014},
slides = {/Talks/Zelazo_CDC2014.pdf},
pdf = {/Publications/Zelazo_CDC14.pdf}
}
- M. Bürger, D. Zelazo, and F. Allgöwer, “On the Steady-State Inverse-Optimality of Passivity-Based Cooperative Control,” in 4th IFAC Workshop on Distributed Estimation and Control in Networked System, Koblenz, Germany, Sep. 2013.



@inproceedings{Mathias2013,
address = {Koblenz, Germany},
author = {B\"{u}rger, Mathias and Zelazo, Daniel and Allg\"{o}wer, Frank},
booktitle = {4th IFAC Workshop on Distributed Estimation and Control in Networked System},
doi = {10.3182/20130925-2-DE-4044.00004},
editor = {Daniel, Vey},
keywords = {conference},
month = sep,
pages = {138--143},
researchtopic = {nds, passivity, nonlinearcontrol, optimization},
title = {{On the Steady-State Inverse-Optimality of Passivity-Based Cooperative Control}},
url = {http://www.ifac-papersonline.net/Detailed/62351.html},
year = {2013},
pdf = {/Publications/Burger_NecSys13.pdf}
}
- S. Schuler, D. Zelazo, and F. Allgöwer, “Robust Design of Sparse Relative Sensing Networks,” in European Control Conference, Zürich, Switzerland, Jul. 2013.




@inproceedings{Schuler2013,
address = {Z\"{u}rich, Switzerland},
author = {Schuler, Simone and Zelazo, Daniel and Allg\"{o}wer, F},
booktitle = {European Control Conference},
doi = {10.23919/ecc.2013.6669618},
keywords = {conference},
pages = {1860--1865},
researchtopic = {nds, optimization},
title = {{Robust Design of Sparse Relative Sensing Networks}},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.23919/ecc.2013.6669618},
year = {2013},
month = jul,
slides = {/Talks/2013_ECC_robust_RSN_design.pdf},
pdf = {/Publications/Schuler_ECC13.pdf}
}
- M. Bürger, D. Zelazo, and F. Allgöwer, “Hierarchical Clustering of Dynamical Networks Using a Saddle-Point Analysis,” IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 58(1):113–124, 2013.



@article{Burger2011_J,
author = {B\"{u}rger, Mathias and Zelazo, Daniel and Allg\"{o}wer, Frank},
doi = {10.1109/TAC.2012.2206695},
issn = {0018-9286},
journal = {IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control},
month = jan,
number = {1},
pages = {113--124},
researchtopic = {nds, optimization},
title = {{Hierarchical Clustering of Dynamical Networks Using a Saddle-Point Analysis}},
url = {http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/lpdocs/epic03/wrapper.htm?arnumber=6228512},
volume = {58},
year = {2013},
pdf = {/Publications/Burger_TAC2013.pdf}
}
- D. Zelazo, S. Schuler, and F. Allgöwer, “Performance and Design of Cycles in Consensus Networks,” Systems & Control Letters, 62(1):85–96, 2013.



@article{Zelazo2011_J,
author = {Zelazo, Daniel and Schuler, Simone and Allg\"{o}wer, Frank},
doi = {10.1016/j.sysconle.2012.10.014},
journal = {Systems \& Control Letters},
month = jan,
number = {1},
pages = {85--96},
researchtopic = {nds, consensus},
title = {{Performance and Design of Cycles in Consensus Networks}},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.sysconle.2012.10.014},
volume = {62},
year = {2013},
pdf = {/Publications/Zelazo_SCL2013.pdf}
}
- S. Schuler, D. Zelazo, and F. Allgöwer, “Design of sparse relative sensing networks,” in 51st IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Maui, HI, Dec. 2012.




@inproceedings{Schuler2012,
address = {Maui, HI},
author = {Schuler, Simone and Zelazo, Daniel and Allg\"{o}wer, Frank},
booktitle = {51st IEEE Conference on Decision and Control},
doi = {10.1109/CDC.2012.6426358},
isbn = {978-1-4673-2066-5},
keywords = {conference},
month = dec,
pages = {2749--2754},
researchtopic = {nds, optimization},
title = {{Design of sparse relative sensing networks}},
url = {http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/lpdocs/epic03/wrapper.htm?arnumber=6426358},
year = {2012},
pdf = {/Publications/Schuler_CDC12.pdf},
slides = {/Talks/CDC2012_Schuler.pdf}
}
- D. Zelazo and F. Allgöwer, “Eulerian Consensus Networks,” in 51st IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Maui, HI, Dec. 2012.




@inproceedings{Zelazo2012a,
address = {Maui, HI},
author = {Zelazo, Daniel and Allg\"{o}wer, Frank},
booktitle = {51st IEEE Conference on Decision and Control},
doi = {10.1109/CDC.2012.6425921},
isbn = {978-1-4673-2066-5},
keywords = {conference},
month = dec,
pages = {4715--4720},
researchtopic = {nds, consensus},
title = {{Eulerian Consensus Networks}},
url = {http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/lpdocs/epic03/wrapper.htm?arnumber=6425921},
year = {2012},
pdf = {/Publications/Zelazo_CDC12_a.pdf},
slides = {/Talks/CDC2012_Zelazo_a}
}
- M. Bürger, D. Zelazo, and F. Allgöwer, “Combinatorial Insights and Robustness Analysis for Clustering in Dynamic Networks,” in American Control Conference, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 2012.



@inproceedings{Burger2012,
address = {Montreal, Canada},
author = {B\"{u}rger, Matthias and Zelazo, Daniel and Allg\"{o}wer, Frank},
booktitle = {American Control Conference},
doi = {10.1109/acc.2012.6314935},
keywords = {conference},
pages = {454--459},
researchtopic = {nds, optimization},
title = {{Combinatorial Insights and Robustness Analysis for Clustering in Dynamic Networks}},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/acc.2012.6314935},
year = {2012},
month = jul,
pdf = {/Publications/Burger_ACC12.pdf}
}
- D. Zelazo, S. Schuler, and F. Allgöwer, “Cycles and Sparse Design of Consensus Networks,” in 51st IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Maui, HI, 2012.




@inproceedings{Zelazo2012d,
address = {Maui, HI},
author = {Zelazo, Daniel and Schuler, Simone and Allg\"{o}wer, Frank},
booktitle = {51st IEEE Conference on Decision and Control},
doi = {10.1109/cdc.2012.6426450},
keywords = {conference},
pages = {3803--3813},
researchtopic = {nds, optimization},
title = {{Cycles and Sparse Design of Consensus Networks}},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/cdc.2012.6426450},
year = {2012},
pdf = {/Publications/Zelazo_CDC12_b.pdf},
slides = {/Talks/CDC2012_Zelazo_b.pdf}
}
- B. Briegel, D. Zelazo, M. Bürger, and F. Allgöwer, “On the Zeros of Consensus Networks,” in 50th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control and European Control Conference, Orlando, FL, Dec. 2011.



@inproceedings{Briegel2011,
address = {Orlando, FL},
author = {Briegel, Benjamin and Zelazo, Daniel and B\"{u}rger, Mathias and Allg\"{o}wer, Frank},
booktitle = {50th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control and European Control Conference},
doi = {10.1109/CDC.2011.6161047},
isbn = {978-1-61284-801-3},
keywords = {conference, consensus},
month = dec,
pages = {1890--1895},
researchtopic = {nds},
title = {{On the Zeros of Consensus Networks}},
url = {http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/lpdocs/epic03/wrapper.htm?arnumber=6161047},
year = {2011},
pdf = {/Publications/Briegel_CDC11.pdf}
}
- M. Bürger, D. Zelazo, and F. Allgöwer, “Network clustering: A dynamical systems and saddle-point perspective,” in 50th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control and European Control Conference, Orlando, FL, Dec. 2011.



@inproceedings{Zelazo2011b,
address = {Orlando, FL},
author = {B\"{u}rger, Mathias and Zelazo, Daniel and Allg\"{o}wer, Frank},
booktitle = {50th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control and European Control Conference},
doi = {10.1109/CDC.2011.6161045},
file = {:Users/danielzelazo/Dropbox/Research/Mendeley Paper Database/B\"{u}rger, Zelazo, Allg\"{o}wer/IEEE Conference on Decision and Control and European Control Conference/B\"{u}rger, Zelazo, Allg\"{o}wer - 2011 - Network clustering A dynamical systems and saddle-point perspective.pdf:pdf},
isbn = {978-1-61284-801-3},
keywords = {conference},
month = dec,
pages = {7825--7830},
researchtopic = {nds, optimization},
title = {{Network clustering: A dynamical systems and saddle-point perspective}},
url = {http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/lpdocs/epic03/wrapper.htm?arnumber=6161045},
year = {2011},
pdf = {/Publications/Burger_CDC11.pdf}
}
- D. Zelazo, M. Bürger, and F. Allgöwer, “A Distributed Real-Time Algorithm for Preference-Based Agreement,” in Proc. 18th IFAC World Congress, Milan, Italy, Aug. 2011.



@inproceedings{Zelazo2011,
address = {Milan, Italy},
author = {Zelazo, Daniel and B\"{u}rger, Mathias and Allg\"{o}wer, Frank},
booktitle = {Proc. 18th IFAC World Congress},
doi = {10.3182/20110828-6-IT-1002.03155},
editor = {Sergio, Bittanti},
keywords = {conference},
month = aug,
pages = {8933--8938},
researchtopic = {nds, optimization},
title = {{A Distributed Real-Time Algorithm for Preference-Based Agreement}},
url = {http://www.ifac-papersonline.net/Detailed/50415.html},
year = {2011},
pdf = {/Publications/Zelazo_IFAC11.pdf}
}
- D. Zelazo and M. Mesbahi, “Graph-Theoretic Analysis and Synthesis of Relative Sensing Networks,” IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 56(5):971–982, 2011.



@article{Zelazo2010_J,
author = {Zelazo, Daniel and Mesbahi, Mehran},
doi = {10.1109/TAC.2010.2085312},
issn = {0018-9286},
journal = {IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control},
month = may,
number = {5},
pages = {971--982},
researchtopic = {nds},
title = {{Graph-Theoretic Analysis and Synthesis of Relative Sensing Networks}},
url = {http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/lpdocs/epic03/wrapper.htm?arnumber=5598522},
volume = {56},
year = {2011},
pdf = {/Publications/Zelazo_TAC2011b.pdf}
}
- D. Zelazo and M. Mesbahi, “Edge Agreement: Graph-Theoretic Performance Bounds and Passivity Analysis,” IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 56(3):544–555, 2011.



@article{Zelazo2009b_J,
author = {Zelazo, Daniel and Mesbahi, Mehran},
doi = {10.1109/TAC.2010.2056730},
issn = {0018-9286},
journal = {IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control},
month = mar,
number = {3},
pages = {544--555},
researchtopic = {nds, graphs, consensus, passivity},
title = {{Edge Agreement: Graph-Theoretic Performance Bounds and Passivity Analysis}},
url = {http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/lpdocs/epic03/wrapper.htm?arnumber=5504814},
volume = {56},
year = {2011},
pdf = {/Publications/Zelazo_TAC2011.pdf}
}
- D. Zelazo and M. Mesbahi, “\mathcalH_∞ Performance and Robust Topology Design of Relative Sensing Networks,” in American Control Conference, Baltimore, MD, Jul. 2010.



@inproceedings{Zelazo2010b,
address = {Baltimore, MD},
author = {Zelazo, Daniel and Mesbahi, Mehran},
booktitle = {American Control Conference},
doi = {10.1109/ACC.2010.5530963},
keywords = {conference},
pages = {4474--4479},
researchtopic = {nds},
title = {{$\mathcal{H}_{\infty}$ Performance and Robust Topology Design of Relative Sensing Networks}},
url = {https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/5530963},
year = {2010},
month = jul,
pdf = {/Publications/Zelazo_ACC10.pdf}
}
- D. Zelazo and M. Mesbahi, “Graph-Theoretic Methods for Networked Dynamic Systems: Heterogeneity and H2 Performance,” in Efficient Modeling and Control of Large-Scale Systems, J. Mohammadpour and K. M. Grigoriadis, Eds. Boston, MA: Springer US, 2010, pp. 219–249.


@incollection{Zelazo,
address = {Boston, MA},
author = {Zelazo, Daniel and Mesbahi, Mehran},
booktitle = {Efficient Modeling and Control of Large-Scale Systems},
doi = {10.1007/978-1-4419-5757-3},
editor = {Mohammadpour, Javad and Grigoriadis, Karolos M.},
isbn = {978-1-4419-5756-6},
keywords = {book},
mendeley-tags = {book},
pages = {219--249},
publisher = {Springer US},
title = {{Graph-Theoretic Methods for Networked Dynamic Systems: Heterogeneity and H2 Performance}},
url = {http://www.springerlink.com/index/10.1007/978-1-4419-5757-3},
year = {2010},
researchtopic = {nds}
}
- D. Zelazo and M. Mesbahi, “\mathcalH_2 Performance of Agreement Protocol with Noise: An Edge Based Approach,” in 48th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control and 28th Chinese Control Conference, Shanghai, China, Dec. 2009.



@inproceedings{Zelazo2009b,
address = {Shanghai, China},
author = {Zelazo, Daniel and Mesbahi, Mehran},
booktitle = {48th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control and 28th Chinese Control Conference},
doi = {10.1109/CDC.2009.5400513},
isbn = {978-1-4244-3871-6},
keywords = {conference, consensus},
month = dec,
pages = {4747--4752},
researchtopic = {nds},
title = {{$\mathcal{H}_2$ Performance of Agreement Protocol with Noise: An Edge Based Approach}},
url = {http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/lpdocs/epic03/wrapper.htm?arnumber=5400513},
year = {2009},
pdf = {/Publications/Zelazo_CDC09.pdf}
}
- D. Zelazo and M. Mesbahi, “\mathcalH_2 Analysis and Synthesis of Networked Dynamic Systems,” in American Control Conference, St. Louis, MO, Jun. 2009.



@inproceedings{Zelazo2009,
address = {St. Louis, MO},
author = {Zelazo, Daniel and Mesbahi, Mehran},
booktitle = {American Control Conference},
doi = {10.1109/ACC.2009.5160153},
isbn = {978-1-4244-4523-3},
keywords = {conference},
pages = {2966--2971},
researchtopic = {nds},
title = {{$\mathcal{H}_2$ Analysis and Synthesis of Networked Dynamic Systems}},
url = {http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/lpdocs/epic03/wrapper.htm?arnumber=5160153},
year = {2009},
month = jun,
pdf = {/Publications/Zelazo_ACC09.pdf}
}
- D. Zelazo and M. Mesbahi, “\mathcalH_2 Performance of Relative Sensing Networks: Analysis and Synthesis,” in AIAA Infotech@Aerospace Conference and AIAA Unmanned ...Unlimited Conference, Seattle, WA, Apr. 2009, no. 7.



@inproceedings{Zelazo2009a,
address = {Seattle, WA},
author = {Zelazo, Daniel and Mesbahi, Mehran},
booktitle = {AIAA Infotech@Aerospace Conference and AIAA Unmanned ...Unlimited Conference},
doi = {10.2514/6.2009-1840},
issn = {1041-1135},
keywords = {conference},
month = apr,
number = {7},
pages = {1-14},
researchtopic = {nds},
title = {{${\mathcal{H}_2}$ Performance of Relative Sensing Networks: Analysis and Synthesis}},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.2514/6.2009-1840},
volume = {21},
year = {2009},
pdf = {/Publications/Zelazo_AIAA09.pdf}
}
- D. Zelazo, “Graph-theoretic Methods for the Analysis and Synthesis of Networked Dynamic Systems,” phdthesis, University of Washington, Department of Aeronautics & Astronautics, 2009.


@thesis{Zelazo2010,
author = {Zelazo, Daniel},
title = {Graph-theoretic Methods for the Analysis and Synthesis of Networked Dynamic Systems},
school = {University of Washington, Department of Aeronautics \& Astronautics},
year = {2009},
type = {phdthesis},
researchtopic = {thesis, nds, consensus},
pdf = {/Theses/Thesis_ZelazoPhD.pdf}
}
- D. Zelazo, A. Rahmani, J. Sandhu, and M. Mesbahi, “Decentralized Formation Control via the Edge Laplacian,” in American Control Conference, Seattle, WA, Jun. 2008.



@inproceedings{Zelazo2008a,
address = {Seattle, WA},
author = {Zelazo, Daniel and Rahmani, Amirreza and Sandhu, Jasmine and Mesbahi, Mehran},
booktitle = {American Control Conference},
doi = {10.1109/ACC.2008.4586588},
isbn = {978-1-4244-2078-0},
keywords = {conference},
month = jun,
pages = {783--788},
researchtopic = {formationcontrol, nds},
title = {{Decentralized Formation Control via the Edge Laplacian}},
url = {http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/lpdocs/epic03/wrapper.htm?arnumber=4586588},
year = {2008},
pdf = {/Publications/Zelazo_ACC08.pdf}
}