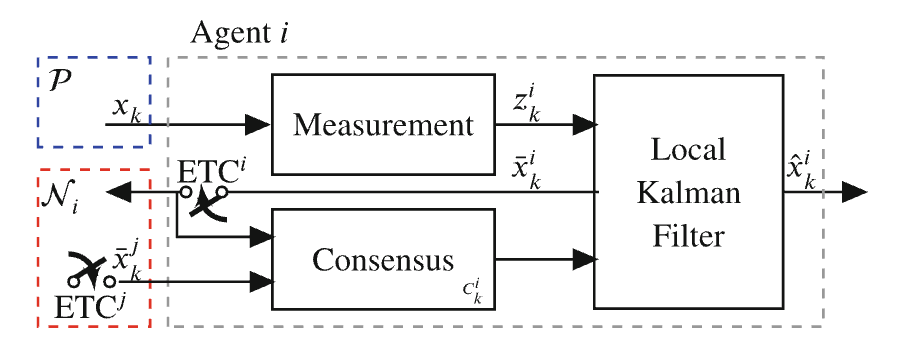
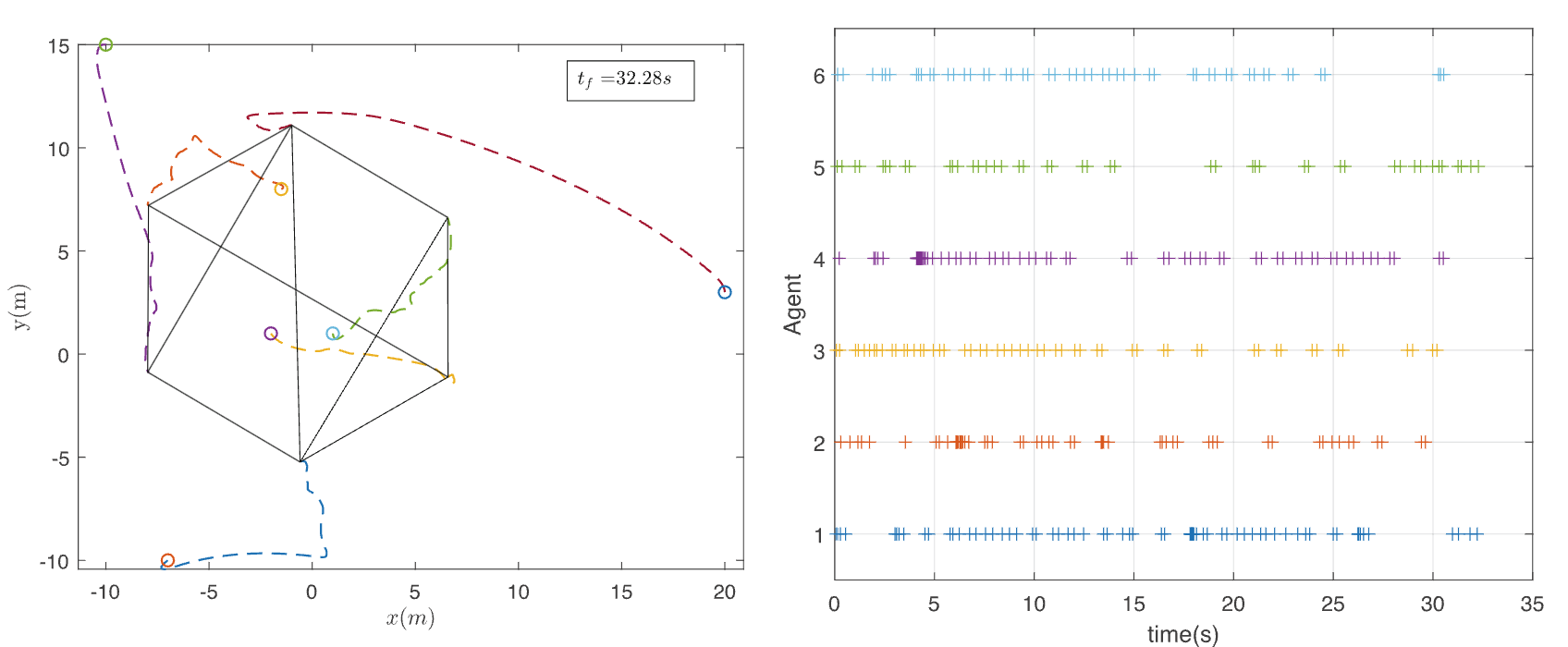
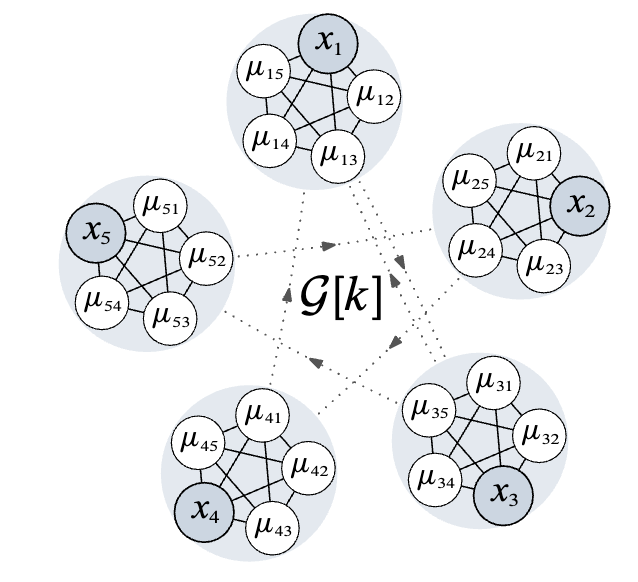
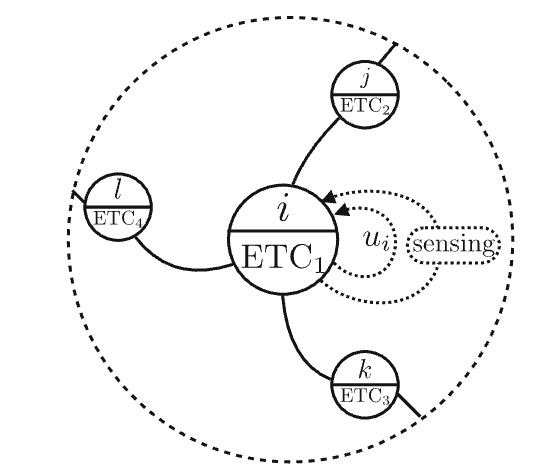
Sensing and communication for autonomous sytsems can be demanding in terms of energy and communication consumption. This problem is amplfied when considering teams of autonomous systems where it may be unreasonable to expect agents to continusouly communicate with other agents. Event-triggered control strategies take a more opportunistic approach for control and estimation of dynamical systems. In a multi-agent setting, agents may not need to communicate continuously in order to sovle the group task. Our research explores how event triggering strategies can be used to solve cooperative control and estimation problems. We consider bearing-based formation control problem, distributed Kalman filtering, and synchronization problems using event or asynchronous strategies.
Related Publications:
- G. Barkai, L. Mirkin, and D. Zelazo, “Asynchronous Sampled-Data Synchronization with Small Communications Delays,” in IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Milan, Italy, Dec. 2024.




@inproceedings{Barkai2024_CDC,
address = {Milan, Italy},
author = {Barkai, Gal and Mirkin, Leonid and Zelazo, Daniel},
booktitle = {IEEE Conference on Decision and Control},
keywords = {conference},
month = dec,
pages = {1619--1624},
researchtopic = {nds, eventtrigger},
title = {{Asynchronous Sampled-Data Synchronization with Small Communications Delays}},
slides = {/Talks/CDC2024_Barkai.pdf},
year = {2024},
doi = {10.1109/CDC56724.2024.10886376},
pdf = {/Publications/Barkai_CDC24.pdf}
}
- G. Barkai, L. Mirkin, and D. Zelazo, “An Emulation Approach to Output-Feedback Sampled-Data Synchronization,” in European Control Conference, Stockholm, Sweden, Jun. 2024.



@inproceedings{Barkai2024_ECC,
address = {Stockholm, Sweden},
author = {Barkai, Gal and Mirkin, Leonid and Zelazo, Daniel},
booktitle = {European Control Conference},
keywords = {conference},
month = jun,
pages = {2610--2615},
researchtopic = {nds,eventtrigger},
title = {{An Emulation Approach to Output-Feedback Sampled-Data Synchronization}},
year = {2024},
slides = {/Talks/ECC2024_Barkai.pdf},
pdf = {/Publications/Barkai_ECC24.pdf}
}
- G. Barkai, L. Mirkin, and D. Zelazo, “Asynchronous Sampled-Data Synchronization with Small communication Delays,” in 63rd Israel Annual Conference on Aerospace Sciences, Haifa, Israel, May 2024.


@inproceedings{Barkai_IACAS2024,
address = {Haifa, Israel},
author = {Barkai, Gal and Mirkin, Leonid and Zelazo, Daniel},
booktitle = {63rd Israel Annual Conference on Aerospace Sciences},
keywords = {conference, consensus},
month = may,
year = {2024},
pages = {},
researchtopic = {nds, eventtrigger},
title = {{Asynchronous Sampled-Data Synchronization with Small communication Delays}},
pdf = {/Publications/Barkai_IACAS2024.pdf}
}
- M. Sewlia and D. Zelazo, “Bearing-Based Formation Stabilization Using Event-Triggered Control,” International Journal on Robust and Nonlinear Control, 34(6):4375–4387, 2024.



@article{Sewlia2023a_J,
author = {Sewlia, Mayank and Zelazo, Daniel},
doi = {10.1002/rnc.7185},
journal = {International Journal on Robust and Nonlinear Control},
keyword = {journal},
month = jan,
volume = {34},
number = {6},
pages = {4375--4387},
researchtopic = {formationcontrol, eventtrigger},
title = {Bearing-Based Formation Stabilization Using Event-Triggered Control},
year = {2024},
url = {https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/rnc.7185},
pdf = {/Publications/Sewlia_IJRNC2022.pdf}
}
- G. Barkai, L. Mirkin, and D. Zelazo, “An emulation approach to sampled-data synchronization,” in IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Singapore, Dec. 2023.



@inproceedings{Barkai2023a,
address = {Singapore},
author = {Barkai, Gal and Mirkin, Leonid and Zelazo, Daniel},
booktitle = {IEEE Conference on Decision and Control},
doi = {10.1109/cdc49753.2023.10384079},
keywords = {conference},
month = dec,
pages = {6449--6454},
researchtopic = {nds, eventtrigger},
title = {{An emulation approach to sampled-data synchronization}},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/cdc49753.2023.10384079},
year = {2023},
pdf = {/Publications/Barkai_CDC2023.pdf}
}
- A. Priel and D. Zelazo, “Distributed Consensus Kalman Filtering Over Time-Varying Graphs,” in IFAC World Congress, Yokohama, Japan, Jul. 2023.




@inproceedings{Priel2023a_C,
address = {Yokohama, Japan},
author = {Priel, Aviv and Zelazo, Daniel},
booktitle = {IFAC World Congress},
doi = {10.1016/j.ifacol.2023.10.903},
keywords = {conference},
month = jul,
pages = {},
researchtopic = {eventtrigger},
title = {{Distributed Consensus Kalman Filtering Over Time-Varying Graphs}},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ifacol.2023.10.903},
year = {2023},
poster = {/Talks/IFAC2023_priel.pdf},
pdf = {/Publications/Priel_IFACWC2023.pdf}
}
- A. Priel and D. Zelazo, “Event-triggered consensus Kalman filtering for time-varying networks and intermittent observations,” International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 33(13):7430–7451, 2023.



@article{Priel2023_J,
author = {Priel, Aviv and Zelazo, Daniel},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1002/rnc.6762},
eprint = {https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/rnc.6762},
journal = {International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control},
keyword = {journal},
keywords = {distributed estimation, event-triggered estimation, multi-agent systems, sensor networks},
month = may,
number = {13},
pages = {7430-7451},
researchtopic = {nds, eventtrigger},
title = {Event-triggered consensus Kalman filtering for time-varying networks and intermittent observations},
url = {https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/rnc.6762},
volume = {33},
year = {2023},
pdf = {/Publications/Priel_IJRNC2023.pdf}
}
- A. Priel, “Consensus Kalman Filtering: Filter Design and Event-Triggering,” mastersthesis, Technion - Israel Institute of Technology, Aerospace Engineering Department, 2022.


@thesis{Priel2022,
author = {Priel, Aviv},
title = {Consensus Kalman Filtering: Filter Design and Event-Triggering},
school = {Technion - Israel Institute of Technology, Aerospace Engineering Department},
year = {2022},
type = {mastersthesis},
researchtopic = {thesis, nds, eventtrigger},
pdf = {/Theses/Thesis_Priel.pdf}
}
- A. Priel and D. Zelazo, “An Improved Distributed Consensus Kalman Filter Design Approach,” in IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Austin, Texas, Dec. 2021.




@inproceedings{Priel2021a,
address = {Austin, Texas},
author = {Priel, Aviv and Zelazo, Daniel},
booktitle = {IEEE Conference on Decision and Control},
doi = {10.1109/cdc45484.2021.9683438},
keywords = {conference},
month = dec,
pages = {502--507},
researchtopic = {eventtrigger, nds},
title = {{An Improved Distributed Consensus Kalman Filter Design Approach}},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/cdc45484.2021.9683438},
year = {2021},
slides = {/Talks/CD2021_Priel.pdf},
pdf = {/Publications/Priel_CDC21.pdf}
}
- M. Sewlia, “Distributed Event-Triggered Control for Multi-Agent Systems with Second-Order Dynamics,” mastersthesis, Technion - Israel Institute of Technology, Aerospace Engineering Department, 2020.


@thesis{Sewlia2020,
author = {Sewlia, Mayank},
title = {Distributed Event-Triggered Control for Multi-Agent Systems with Second-Order Dynamics},
school = {Technion - Israel Institute of Technology, Aerospace Engineering Department},
year = {2020},
type = {mastersthesis},
researchtopic = {thesis, formationcontrol, eventtrigger},
pdf = {/Theses/Thesis_Sewlia.pdf}
}
- M. Sewlia and D. Zelazo, “Distributed Event-Based Control for Second-Order Multi-Agent Systems,” in 27th Mediterranean Conference on Control and Automation, Akko, Israel, Jul. 2019.



@inproceedings{Sewlia2019a,
address = {Akko, Israel},
author = {Sewlia, Mayank and Zelazo, Daniel},
booktitle = {27th Mediterranean Conference on Control and Automation},
doi = {10.1109/med.2019.8798577},
keywords = {conference},
month = jul,
pages = {304--309},
researchtopic = {eventtrigger},
title = {{Distributed Event-Based Control for Second-Order Multi-Agent Systems}},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/med.2019.8798577},
year = {2019},
pdf = {/Publications/Sewlia_MED19.pdf}
}